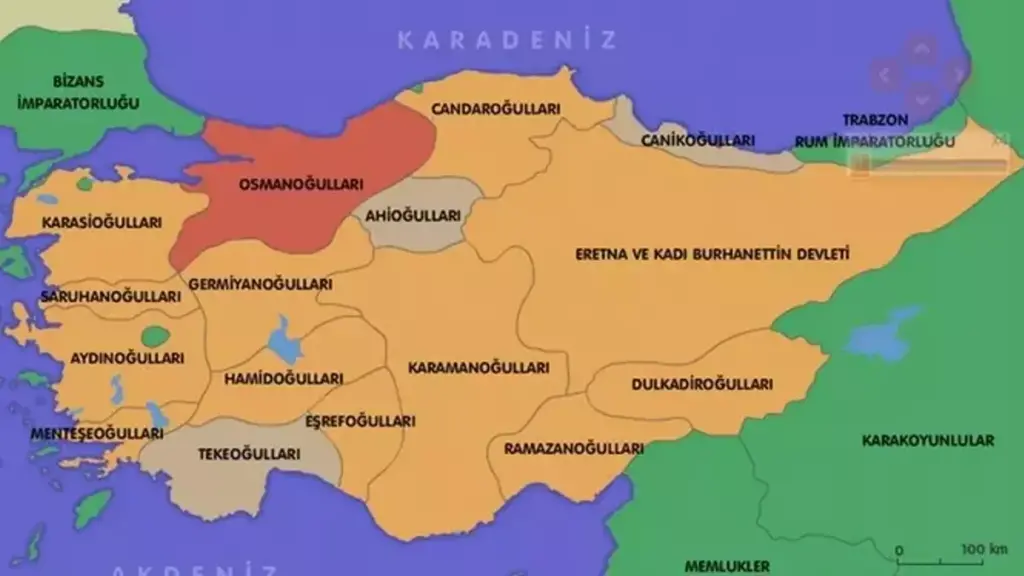
Before the rise of the Ottoman Empire, the geography of Anatolia was ruled by many important principalities. This period is known as the Pre-Ottoman Principalities and forms the basis of Turkey’s emergence on the historical stage. Before the magnificent rise of the Ottoman Empire, these principalities ruled over their lands and shaped the political, cultural and social fabric of the region. The Pre-Ottoman Principalities period is of vital importance to understanding the rich history of Anatolia. In this content, we will explore the most important principalities of the pre-Ottoman period and the legacy they left behind. The traces of the Pre-Ottoman Principalities on the historical stage help us understand the roots and cultural diversity of Turkey.
I. Seljuk Principality and Its Heritage
In the period considered to be before the Ottoman Empire, a large part of Anatolia was under the rule of the Great Seljuk Empire. However, with the weakening of the Seljuk Empire, various principalities emerged in Anatolia and one of these principalities, the Anatolian Seljuk State, became an important power in the region.
The Anatolian Seljuk State was founded in 1077 and covered a large part of Anatolia. The state, whose capital was Iznik, was founded by Seljuk Turks of Central Asian origin. The Seljuks adopted Islam and acted under the auspices of the Abbasid Caliphate.
Kutalmışoğlu Süleyman Şah, who is considered the founder of the Anatolian Seljuk State, took the first steps of Turkish domination in Anatolia. During Süleyman Şah’s rule, Turkmen tribes were allowed to settle in Anatolia and the Turkification of the region accelerated.
The brightest period of the Anatolian Seljuk State was the period of Alaeddin Keykubad I. Keykubad strengthened the state politically and economically and turned the capital Konya into a center of culture and art. During this period, the borders of the Anatolian Seljuk State expanded and a large part of Anatolia came under Seljuk control before the Mongol invasion.
The Anatolian Seljuk State also represents an important period in the field of architecture and art. Seljuk architecture includes many structures such as mosques, madrasahs, caravanserais and castles. These structures present the most beautiful examples of Seljuk art and have survived to the present day. In particular, the Divriği Great Mosque and Hospital in Sivas is one of the most important works of Anatolian Seljuk architecture.
In the last period of the Anatolian Seljuk State, the state weakened due to the Mongol invasion and the pressure of the Ilkhanate. During this period, political instability began in Anatolia with the strengthening of the principalities. In 1308, the Anatolian Seljuk State officially ended and was accepted as the beginning of the Principalities Period.
As a result, the Anatolian Seljuk State is considered the forerunner of the Ottoman Empire. It played an important role in the settlement of Turks in Anatolia and the Turkification of the region, spreading Islam to Anatolia and enriching the region culturally. The legacy of the Anatolian Seljuk State has shaped the historical and cultural identity of today’s Turkey.
II. The Danishmendids Principality: A Power in the North of Anatolia
The Danishmends Principality was an important Turkish principality that was influential in the north of Anatolia during the pre-Ottoman Principalities period. This principality, which existed in the 11th and 12th centuries, ruled especially in the regions close to the Black Sea and influenced the political balance of the region.
Establishment and Rise
The Danishmendliler Principality was founded by Danishmendlü Süleyman Şah in the 1080s. Taking advantage of the weakening of the Seljuk Empire, Danishmendlü Süleyman Şah declared independence and took control of Amasya. He then established Sivas, the capital of the Danishmendliler Principality, and moved the center of the principality there.
The Danishmends gained economic strength by controlling a significant portion of the trade routes in Anatolia. In particular, control of the port cities in the regions close to the Black Sea increased the economic and strategic importance of the principality.
The Administration and Cultural Influence of the Danishmends
During the rule of the Danishmendler Principality among the principalities before the Ottomans , the spread of Turkish culture and Islam accelerated with the increase of Turkmen settlements in the region. This process, which began during the reign of Danishmendler Süleyman Şah, continued throughout the existence of the Danishmendler Principality.
During the Danishmend period, many important works were built in Anatolia and this period contributed to the architectural and cultural enrichment of Anatolia. Many structures such as mosques, madrasahs, caravanserais and castles have carried the legacy of the Danishmend period to the present day.
Decline and Aftermath
The Danishmend Principality was weakened over time in the struggles with the Seljuks and other neighboring principalities and came under the control of the Anatolian Seljuks in 1177. However, the legacy of the Danishmends is still felt in the cultural and historical fabric of Anatolia. The works and cultural influences left by the principality constitute an important part of the rich historical heritage of Anatolia.
As a result, the Danishmendler Principality continued its existence as an important political and cultural power in the north of Anatolia and influenced the historical course of the region. It played an important role in the spread of Turkish culture and Islam to Anatolia and left behind valuable works in the field of architecture and art. The Danishmendler Principality enriched the historical identity of Anatolia as an important part of the pre-Ottoman period.
III. Mengucoğulları Principality and the South of Anatolia
The Mengucoğulları Principality was an important Turkish principality that was influential in the south of Anatolia during the pre-Ottoman Principalities period. They particularly ruled in the region where today’s Adana, Mersin and Osmaniye are located. The Mengucoğulları took control of the trade routes in the south of Anatolia and became economically powerful in the region.
Establishment and Rise
The founder of the Mengucoğulları Principality was Mengucek Gazi. Mengucek Gazi became an important power in Southeastern Anatolia in the early 11th century and gradually took control of Adana and its surroundings. Mengucek Gazi, the leader of the Menguclu Turkmen tribes, encouraged Turkmen settlements in the region and increased the power of the principality.
Adana, the capital of the Mengüçoğulları Principality, became an important economic center due to its location at the intersection of trade routes. Thanks to this strategic location, the principality became the center of trade in southern Anatolia and grew economically.
Management and Cultural Influence
During the rule of the Mengucoğulları Principality, the spread of Turkish culture and Islam in the region accelerated. The principality, especially because it was located on trade routes, served as a bridge between different cultures and increased the cultural diversity of the region.
During the Mengüçoğulları period, many important structures were built in the region and the cultural influence of the principality has survived to the present day. Many structures such as mosques, madrasahs, caravanserais and castles have carried the heritage of the Mengüçoğulları Principality to the present day. These structures contributed to the architectural and cultural enrichment of Anatolia.
Decline and Aftermath
The Mengucoğulları Principality weakened over time in struggles with neighboring principalities and came under the control of the Anatolian Seljuks in the late 13th century. However, the cultural and economic influence of the principality continued in the region and the legacy of the Mengucoğulları is still felt today.
As a result, among the principalities before the Ottomans, the Mengucoğulları Principality continued its existence as an important political and economic power in the south of Anatolia and influenced the historical course of the region. The principality played an important role in the spread of Turkish culture and Islam to the region and left valuable works in the field of architecture and art. The Mengucoğulları Principality enriched the historical identity of Anatolia as an important part of the pre-Ottoman period.
IV. Artuqids Principality: A Peak in Art and Culture
The Artuqids were a Turkish principality that was influential in the eastern part of Anatolia during the pre-Ottoman principalities and had a significant peak in art and culture. They ruled in cities such as Malatya, Elazığ and Diyarbakır, especially in the 11th and 12th centuries. The Artuqids played an important role in Islamic art and literature and brought their own unique style to the region.
Establishment and Rise
The Artuqids were founded by Artuk Bey in the early 11th century. Artuk Bey served the Seljuk sultans and seized political authority in the region. The Artuqids, who took control of Malatya and its surroundings, also established dominance in Elazığ, Diyarbakır and its surroundings over time.
The Artuqids continued their existence as a principality under the Seljuk Empire, but over time they declared independence and established their own administration. During this period, the principality’s economy developed based on agriculture and trade, and the prosperity of the region increased.
Management and Cultural Influence
During the rule of the Artuqids, there was a significant development in art and culture in the region. The principality encouraged the production of important works in different fields of Islamic art, thus ensuring the artistic enrichment of the region.
During the Artuqid period, many important structures were built in the region and these structures have survived to the present day. Many structures such as mosques, madrasahs, caravanserais and palaces carry the legacy of the Artuqid Principality to the present day. These structures have made significant contributions to the architectural and cultural enrichment of Anatolia.
Decline and Aftermath
The Artuqids Principality weakened over time due to the Mongol invasion and other internal and external threats. The principality came under the control of the Seljuk Empire in the late 12th century. However, the cultural heritage of the Artuqids continued in the region and had a great impact on the artistic and cultural life of Anatolia during the Ottoman period.
As a result, the Artuqids reached a significant peak in art and culture in the east of Anatolia and shaped the historical identity of the region. The principality contributed to the development of Islamic art and left important works in the fields of architecture and literature. The Artuqids, as an important part of the pre-Ottoman period, enriched the art and culture life of Anatolia.
V. Ayyubids: The Fight Against the Crusaders and the Liberation of Anatolia
The Ayyubids are known as an important Muslim Turkish principality during the Pre-Ottoman Principalities period. They were influential in the Middle East and Anatolia in the 12th and 13th centuries. The Ayyubids defended the Islamic world by fighting against the Crusaders, especially during the Crusades, and made significant contributions to the liberation of Anatolia.
Establishment and Rise
The Ayyubids were established in Egypt under the leadership of Saladin in the early 12th century. Saladin was an important leader in the fight against the Crusaders and took back Jerusalem from the Crusaders. After Saladin’s death, the Ayyubids became an important power in the Islamic world and took control of many regions.
Fighting the Crusaders
The Ayyubids achieved important victories in the fight against the Crusaders and protected the Islamic world. In 1187, in the Battle of Hattin, the Ayyubid army under the command of Saladin defeated the Crusaders and took back Jerusalem. This victory increased the prestige of the Ayyubids in the Islamic world and shook the Crusaders’ dominance in the region.
The Ayyubids not only achieved military victories in their struggles with the Crusaders, but also attracted attention with their political and diplomatic skills. Thanks to the treaties and agreements made with the Crusaders, the Ayyubids protected and strengthened the Islamic communities in the region.
Liberation of Anatolia
The Ayyubids also played an important role in the liberation of Anatolia. In the mid-12th century, with the weakening of the Anatolian Seljuks, Ayyubid emirates were established in various regions of Anatolia. These emirates played an important role in the Islamization and Turkification of Anatolia.
The Ayyubids ensured the political and military balance in the region through the emirates they established in Anatolia and prevented the Crusaders from spreading into Anatolia. In addition, the Ayyubids’ presence in Anatolia encouraged the settlement of Turkmen tribes in the region and accelerated the Turkification of Anatolia.
As a result, the Ayyubids preserved the unity of the Islamic world with their courage and resistance in the fight against the Crusaders and made significant contributions to the liberation of Anatolia. The Ayyubids’ presence in Anatolia contributed significantly to the Islamization and Turkification of the region. As an important part of the pre-Ottoman period, the Ayyubids shaped the historical and cultural identity of Anatolia and made great contributions to the development of Turkish Islamic civilization.
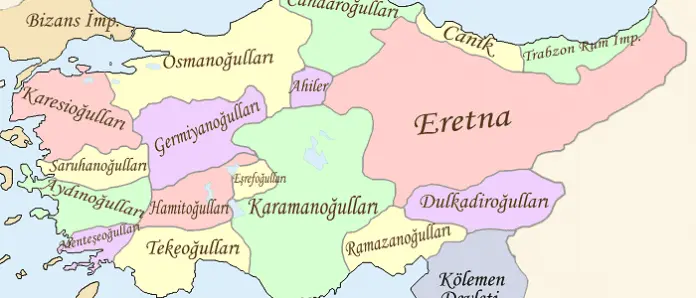
Legacy of the Principalities Before the Ottomans
The rise of the Ottoman Empire is one of the brightest periods in Anatolia’s history. However, before the rise of this enormous empire, the Pre-Ottoman Principalities period was an important phase that formed the roots of Anatolia. During this period, various principalities ruled all over Anatolia and shaped the political, cultural and social fabric of the region.
The principalities before the Ottomans played a critical role in the process of Turkification and Islamization of Anatolia. These principalities spread Islam to Anatolia, strengthened the roots of Turkish culture and formed the historical identity of the region.
Among the principalities established in different regions of Anatolia, there are important names such as the Anatolian Seljuk State, the Danishmendids Principality, the Mengüçoğulları Principality, the Artukoğulları Principality and the Ayyubids. These principalities contributed to the rich historical heritage of Anatolia with their architectural works, works of art and cultural interactions.
The period of pre-Ottoman principalities is of vital importance to understand the origins of the Ottoman Empire. The legacy of these principalities played a decisive role in the rise of the Ottoman Empire and the historical course of Anatolia. Today, traces of the pre-Ottoman principalities can still be seen all over Anatolia, and the legacy left by these principalities makes a significant contribution to the historical richness of Turkey. The pre-Ottoman principalities should be remembered as an important stone that forms the cultural mosaic of Anatolia.